Navigate BioPharma Services Spectral Flow TNK Profiling Assay Method Summary
Intended Use
The 28-parameter comprehensive T cell and NK cell assay was meticulously designed to evaluate critical functional states of T cells and NK cells in patients receiving immunotherapies. In clinical trials, the identification and monitoring of immune cell biomarkers are pivotal for understanding disease mechanisms and therapeutic responses. The assay uses two million peripheral blood mononuclear cells in a single tube and provides quantitative information on functional states (e.g., proliferation, differentiation, regulation and activation) of T cell, NK cells and NK-T cells in addition to frequencies of various lymphocyte subsets critical for understanding the efficacy of immunotherapies (Martner 2015; Kamphorst 2017) (Figure 1).
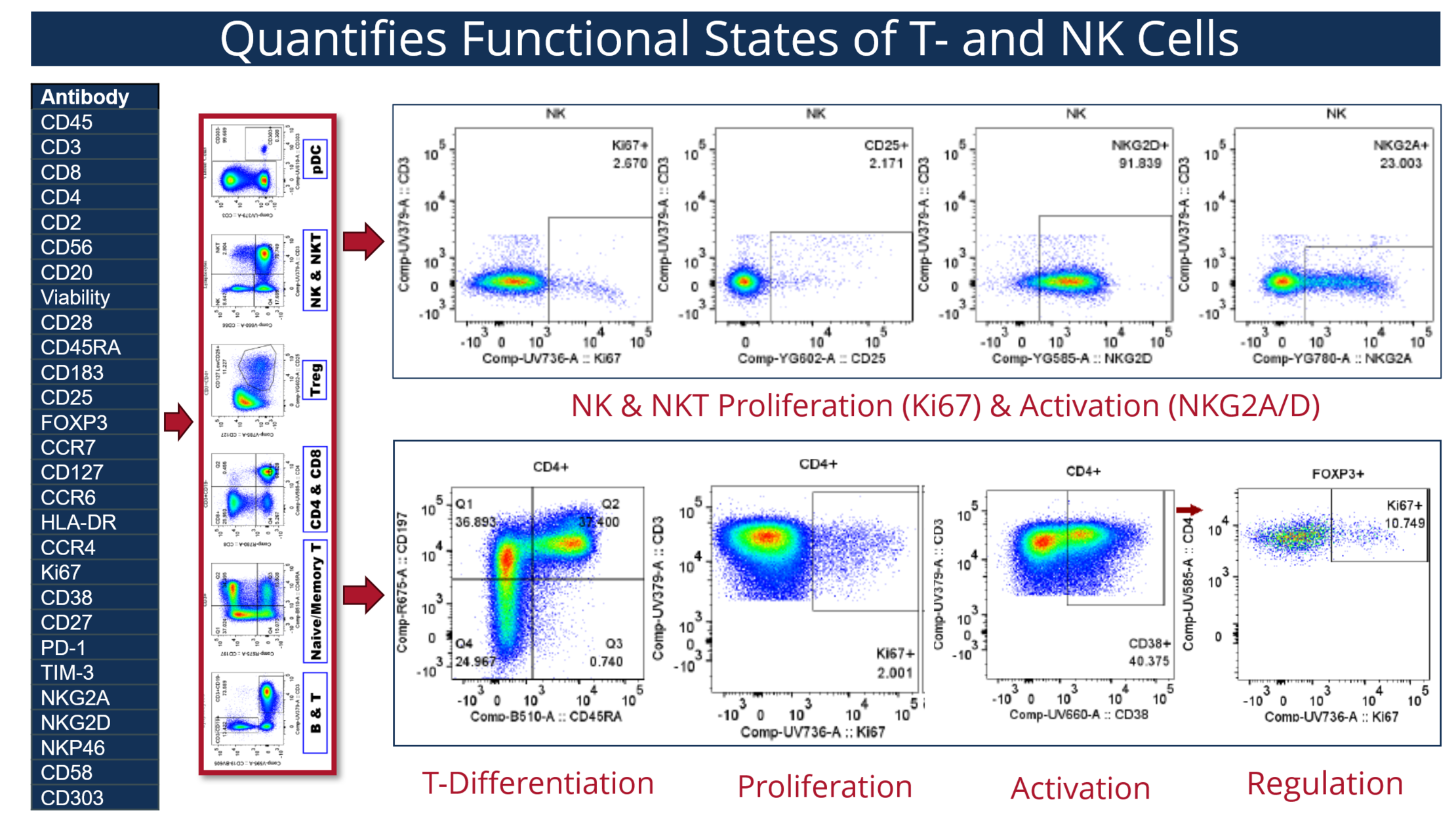
Figure 1: Overview of Spectral flow TNK Profiling assay depicting interrogatable biomarkers, lymphocyte lineages and their functional states
Method Background and Design Principles
The 28-parameter comprehensive TNK assay utilizes a robust panel of markers, including CD45, CD3, CD8, CD4, CD2, CD56, CD20, and viability dyes, to extensively evaluate both T cells and NK cells. This assay measures T cell activation through markers such as CD25, CD28, HLA-DR, and CD38, and assesses NK cell activation using CD56, NKG2D, NKp46, and NKG2A. Proliferation states are determined via Ki-67 expression, while cell differentiation is traced using CD45RA and CCR7. Furthermore, the assay examines exhaustion states by identifying inhibitory receptors like PD-1 and TIM-3. Additional markers such as CD127, CCR4, CCR6, CD183 (CXCR3) and FoxP3 are used to delineate regulatory T cells, T helper (Th) cells and memory subsets, and CD27 and CD58 provide further granularity in defining cell subsets. This comprehensive approach allows for an in-depth analysis of activation, proliferation, and exhaustion states, offering valuable insights for detailed immunophenotyping and biomarker monitoring in clinical and research settings.
This assay not only allows the analysis of multiple T and NK cell subsets simultaneously but also provides a better understanding of the immune response before and after treatment in patients enrolled in clinical trials. As a result, it contributes to a deeper understanding of disease processes, immune response patterns, and treatment outcomes.
High complexity panels, like our TNK panel, have the added benefit of identifying rare and complex cell populations, which may play critical roles in various diseases and immunological responses. This capability enables researchers to not only gain insights into these cell populations but also to identify potential novel biomarkers that may have predictive or prognostic value.
Given the limited availability of clinical specimens and the challenges associated with collecting blood from fragile patients, a single-tube high-dimensional assay offers a significant advantage by reducing the requirement for a large volume of blood to run multiple flow cytometry assays. This streamlined approach not only saves time and resources but also allows for a more efficient utilization of limited clinical samples (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Overview of clinical trial specimen handling and analyses workflow at our laboratory
Analytical Performance Summary
The assay validation process focused on evaluation of specificity, sensitivity (LLOQ, LOD, & LOB) and precision as key criteria for assessing the performance of the assay. The analytical validation plan was designed based on principles described in CLSI H62, Validation of Assays Performed by Flow Cytometry. The results of the assay validation activities are summarized in Table 1 and complete details are described in an independent assay validation report.
Table 1. 28-plex TNK Spectral Flow Method Validation Summary
Parameter | Acceptance Criteria | Result | Pass/Fail |
|---|---|---|---|
| Functional Sensitivity (LLOQ) | Lowest dilution at which the CV in triplicate measurements varies by ≤ 25%) | Among all specimens tested, a CV ≤ 25% was observed in all triplicate intra-assay measurements for target biomarker populations measured above LOD | LLOQ defined with a minimum of 83 events |
| Intra-Assay Precision | Number of events (cell counts) of all triplicates should not show more than 25% CV, 35% at near LLOQ | Low frequency populations (low cell counts) showed a maximum CV of <25% | Pass |
| Inter-Instrument Precision | Pass | ||
| Inter-Operator Precision | Pass | ||
| Inter-Assay Precision | Pass | ||
| Specificity | Assay clearly identifies intended biomarker subsets | All intended target subsets were clearly identified | Pass |
Discussion
The validation data summarized in this document provide robust evidence that the 28-parameter TNK assay meets the stringent analytical performance standards recommended by clinical cytometry consortia and CLSI H62 guidance documents. Furthermore, the utilization of a comprehensive set of markers known to be significant in immune function and disease prognosis ensures that the results generated by this assay are reliable and actionable. These markers, which include indicators of lymphocyte activation, proliferation, maturation and regulation have been previously demonstrated to correlate with immunotherapy clinical outcomes. The data summarized here provide assurance that the 28-parameter TNK assay validated at Navigate BioPharma's laboratory is suitable for detailed immunophenotyping and precise monitoring of lymphocyte subpopulations in clinical trials, ultimately contributing to the development of more effective and personalized therapies.
References
T-cell Invigoration to Tumour Burden Ratio Associated with Anti-PD-1 Response. 1st ed. Nature, 2017.
NK Cell Expression of Natural Cytotoxicity Receptors May Determine Relapse Risk in Older AML Patients Undergoing Immunotherapy for Remission Maintenance. Oncotarget, 2015.
Proliferation of PD-1+ CD8 T cells in Peripheral Blood after PD-1-Targeted Therapy in Lung Cancer Patients. PNAS, 2017.